The Python int() function is an essential tool for converting floating-point numbers or strings into integers. Handling numbers in Python is a frequent task, and in this post, we will explore the detailed usage of the int() function in Python.
Table of Contents
What is the Python int() Function?
The int() function in Python is used to convert a value to an integer. An integer is a number without a decimal point. The int() function is typically used to convert other data types, such as strings or floating-point numbers (floats), into integers.
For example, to convert the string "123" to the number 123, you would use int("123"). In this way, int() is a highly useful function for number conversion tasks.
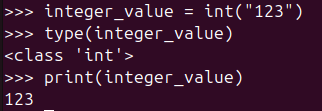
integer_value = int("123")
type(integer_value)
print(integer_value)In the result below, you can see that the string "123" has been converted into the integer 123. Let’s dive into how you can practically use the int() function.
Basic Usage of the int() Function
Converting Strings to Integers
In Python, you use the int() function to convert a number represented as a string into an integer. This is especially useful when receiving user input, such as converting an entered age into an integer.
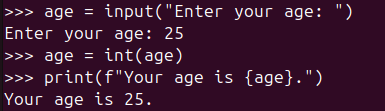
age = input("Enter your age: ")
age = int(age)
print(f"Your age is {age}.")The input() function always returns a string, so it’s necessary to convert the input value to an integer using int() when performing calculations.
Converting Floats to Integers
The int() function can also convert a float (a decimal number) into an integer. In this process, the decimal part is discarded. That is, int() removes the decimal point and returns only the integer portion of the number.
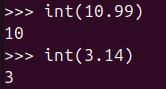
int(10.99)
int(3.14)Keep in mind that since the decimal part is simply discarded, no rounding is performed.
Base Conversion
The int() function allows you to specify a base as a second argument. By default, it operates in base 10 (decimal), but you can also work with other number systems like binary (base 2), octal (base 8), and hexadecimal (base 16). This feature is especially useful in computer systems or network programming.
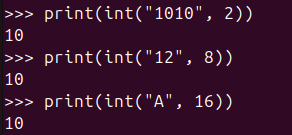
print(int("1010", 2))
print(int("12", 8))
print(int("A", 16))As shown above, you can easily handle various number formats through base conversion. In the image below, binary 1010, octal 12, and hexadecimal A are all converted to decimal 10.
Caution: Values That Cannot Be Converted
Not all strings can be converted to integers. For example, a string like "hello" cannot be converted into a number, and attempting to do so will raise an error like ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: 'hello'. Therefore, when using the int() function, it’s crucial to ensure that the value to be converted is in a numerical format.
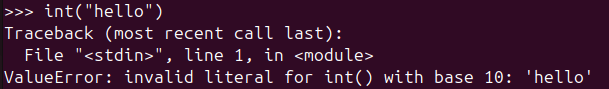
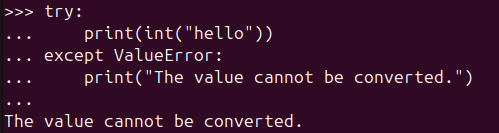
You can handle non-convertible values safely by using a try-except block, as shown in the code below:
try:
print(int("hello"))
except ValueError:
print("The value cannot be converted.")In the image below, you can see how the exception is handled safely without triggering a ValueError message.
Summary
The Python int() function is a highly useful tool for converting data such as strings and floats into integers. Beyond basic usage, it can be employed for base conversions, data validation, and many other applications. This makes it an essential function, especially in situations where you need to handle large-scale data processing or validate user input. However, you must be mindful of non-convertible values that may raise errors, and prepare to handle such cases in advance.
Now that you have a thorough understanding of the various features and uses of the int() function, you can write more efficient Python code. While simple, the int() function is incredibly powerful.
